

Isolation and extraction of blunted vector fragment- I gel purified my fragment by freeze-thaw, ethanol precipitated the DNA, and resuspended in 20 uL CIAP buffer (NEB 3). I then heat inactivated Klenow by heating at 75 C for 20 minutes. I just wanted to be on the super-safe side.įill-in Reaction- I added 2 uL of Klenow (NEB: 3'-5' exo-) and 1 uL of 2.5 mM dNTPs and incubated at 37 C for 30 minutes. In fact, it really wouldn't have mattered if I didn't heat inactivate them because the blunting reaction wouldn't have recreated their recognition sites. I was lucky that both NdeI and BsrGI can be heat inactivated.
I inactivated the restriction enzymes by first upping the salt to 100mM and then heating at 80 C for 20 minutes. I incubated the reaction for 2 hours at 37 C and ran 1 uL to check for completion of the digest. Preparation of vector- I cut my vector DNA with NdeI and BsrGI in a 50 uL reaction containing NEB 4. Also, I didn't care which way my fragment my fragment went in. I would avoid doing a blunt end ligation if you can find compatible enzymes or can add handy cleavage sites by PCR.
*Considerations* There simply wasn't another way to achieve the right construct without doing it this way. I read everything I could about the topic on this forum and came up with the following protocol, which, worked really well. I have recently performed a successful ligation using Klenow to make blunt ends.
#Klenow fragment neb how to#
Ones 1 in 72 colonies and many times I just have nothing !! I wish someone could give me some good advices or show me how to do it with better results! Ones, I had 5 positive colonies in 48 I picked. Ones of them, incubating 15 min, the other one, 4 or 6 h at 25Â☌ both (I inactive the first one at 70Â☌ 20 min to wait for the second one).
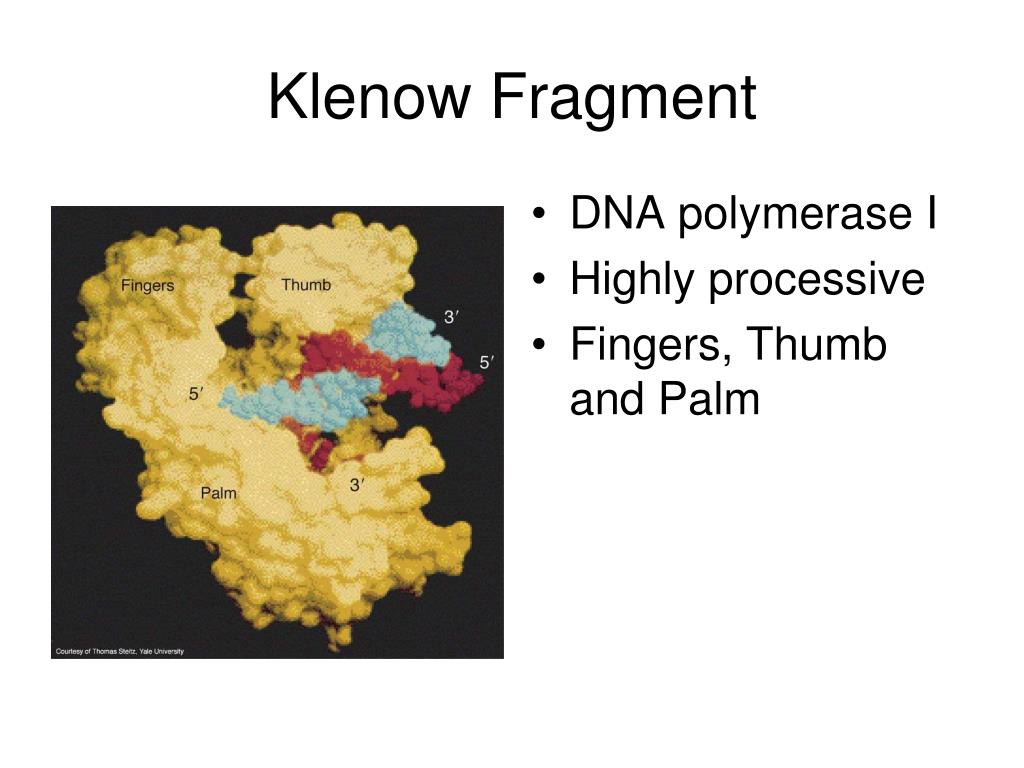
Two tubes kenow (NEB) treatment using twice that NEB recommends but no more in any NEB restriction buffer and dNTPs at 50 uM. Gel-purification (if I don’t do that, I have some or many colonies in my c(-). Digest my DNA (a good amount), phenol-chlorof extraction (I think it wouldn’t be necessary, but I do as my boss recommends). What I have done with the best results is: I have try many different conditions!!!! Temperature, klenow concentration, incubation time. She says it’s very important a Phenol-Chloroform extraction before and after klenow treatment and she says she incubated at 37Â☌ over night. I have try it many times with very few successful cases.īy boss says she did it many times (I don’ t know). I’m suffering a lot because I have to fill in many different thing (The reason? A long story ). I’m going to talk about my experience…. The exo-Klenow fragment is used in some fluorescent labeling reactions for microarray, and also in dA and dT tailing, an important step in the process of ligating DNA adapters to DNA fragments, frequently used in preparing DNA libraries for Next-Gen sequencing.I don’t think I could help you very much. This form of the enzyme is called the exo- Klenow fragment. This results in forms of the enzyme being expressed that retain 5' → 3' polymerase activity, but lack any exonuclease activity (5' → 3' or 3' → 5'). This problem can be overcome by introducing mutations in the gene that encodes Klenow. Just as the 5' → 3' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase I from E.coli can be undesirable, the 3' → 5' exonuclease activity of Klenow fragment can also be undesirable for certain applications. The Klenow fragment was also the original enzyme used for greatly amplifying segments of DNA in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process, before being replaced by thermostable enzymes such as Taq polymerase. Filling in receded 3' ends of DNA fragments to make 5' overhang blunt.Synthesis of double-stranded DNA from single-stranded templates.The Klenow fragment is extremely useful for research-based tasks such as: coli makes it unsuitable for many applications, the Klenow fragment, which lacks this activity, can be very useful in research. 5' → 3' polymerase activity, and 3' → 5' exonuclease activity).īecause the 5' → 3' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase I from E. coli is cleaved by subtilisin retains the 5' → 3' exonuclease activity but does not have the other two activities exhibited by the Klenow fragment (i.e. The other smaller fragment formed when DNA polymerase I from E. First reported in 1970, it retains the 5' → 3' polymerase activity and the 3’ → 5’ exonuclease activity for removal of precoding nucleotides and proofreading, but loses its 5' → 3' exonuclease activity. coli is enzymatically cleaved by the protease subtilisin. The Klenow fragment is a large protein fragment produced when DNA polymerase I from E. Functional domains in the Klenow Fragment (left) and DNA Polymerase I (PDB).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
